Skin Cancer
We provide expert surgical care for skin cancer, focusing on safe removal and aesthetic reconstruction for optimal healing.
Skin Cancer
Skin cancer is a disease where abnormal skin cells grow uncontrollably, potentially invading other parts of the body. It’s caused by damage to skin cells, often from ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or tanning beds. The most common types are basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma, while melanoma is the most dangerous. Early detection and treatment are crucial for successful outcomes.
Types of Skin Cancer
The most common type, usually slow-growing, and often appears as a pearly or waxy bump.
Can appear as a firm, red nodule or a flat lesion with a scaly, crusted surface.
The most serious type, often developing from moles, and can spread quickly.
Get a Free Consultation
Book your free consultation today and take the first step toward expert care. Our specialists are here to guide you with personalized treatment options.
Causes and Risk Factors
UV Radiation: Exposure to sunlight and tanning beds is the primary cause.
Family History: Having a family history of skin cancer increases the risk.
Skin Type: Fair skin and light eyes are more susceptible.
Age: The risk of skin cancer increases with age.
Immune System Weakness: Individuals with weakened immune systems are at higher risk.
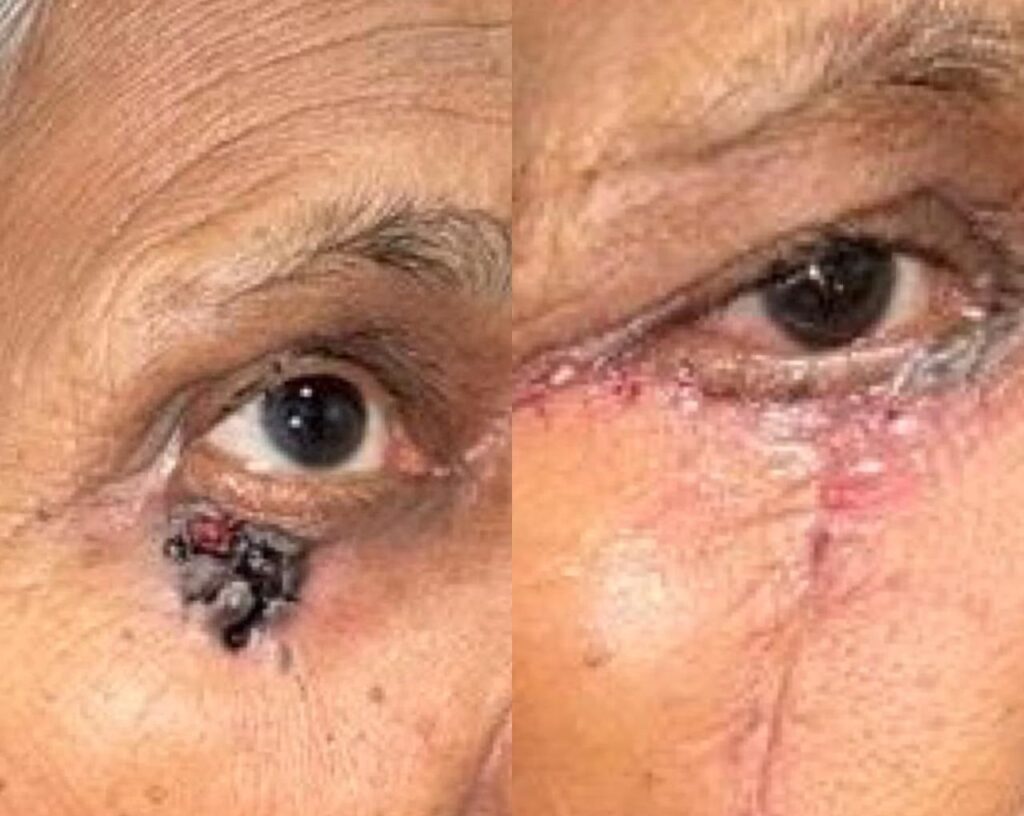
Symptoms
A new spot on the skin or a change in size, shape, or color of an existing spot.
A sore that doesn’t heal or keeps bleeding.
A new bump or growth, often with a pearly or waxy appearance.
A red, scaly patch.
Prevention
Sun Protection: Limit sun exposure, especially during peak hours.
Sunscreen: Use broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher.
Protective Clothing: Wear hats, long sleeves, and pants when outdoors.
Regular Skin Checks: Check your skin regularly for any changes.
Professional Skin Exams: Get regular skin exams from a dermatologist, especially if you have a family history of skin cancer.
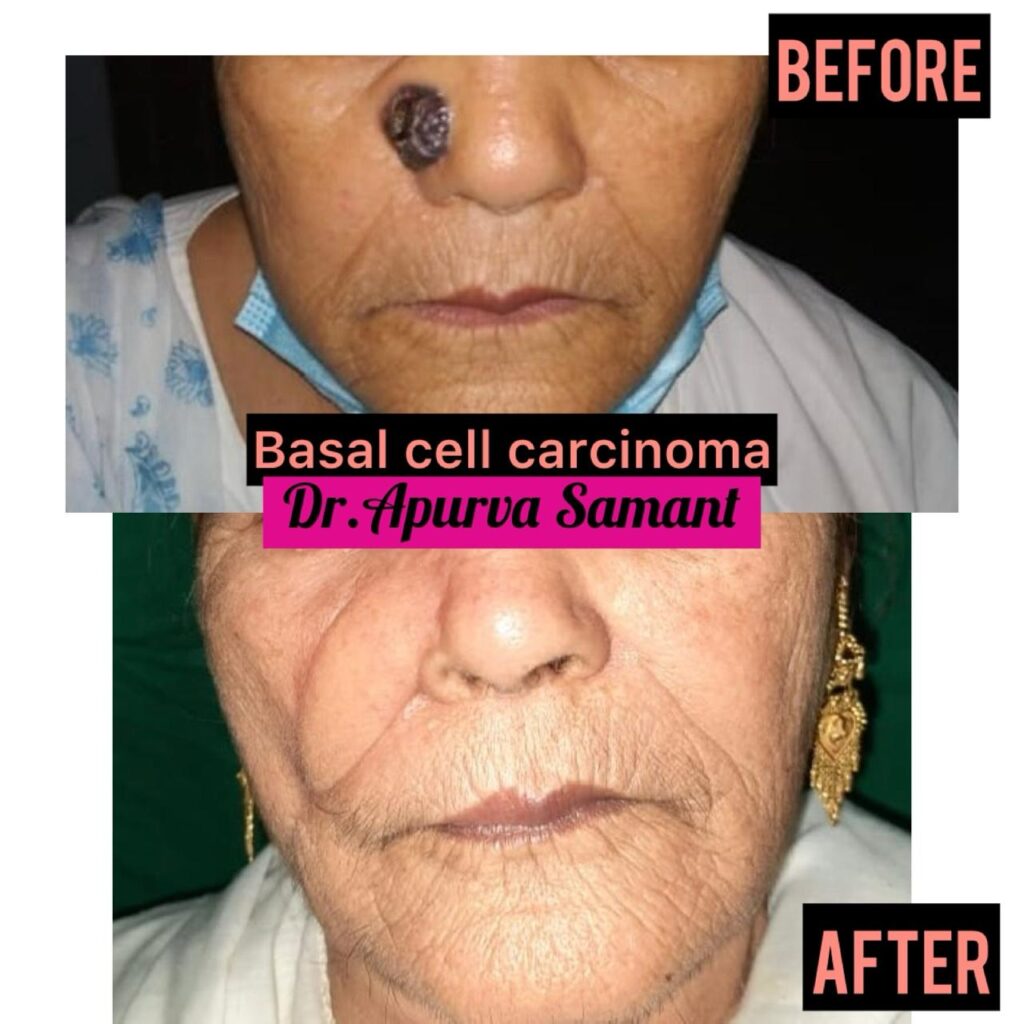
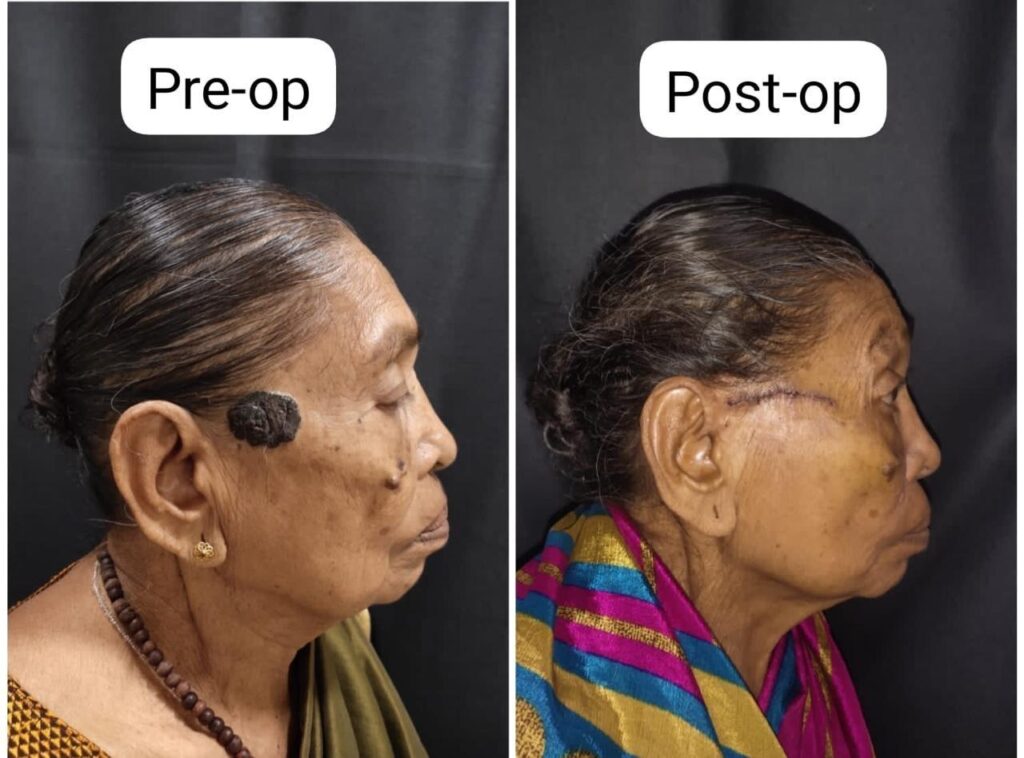
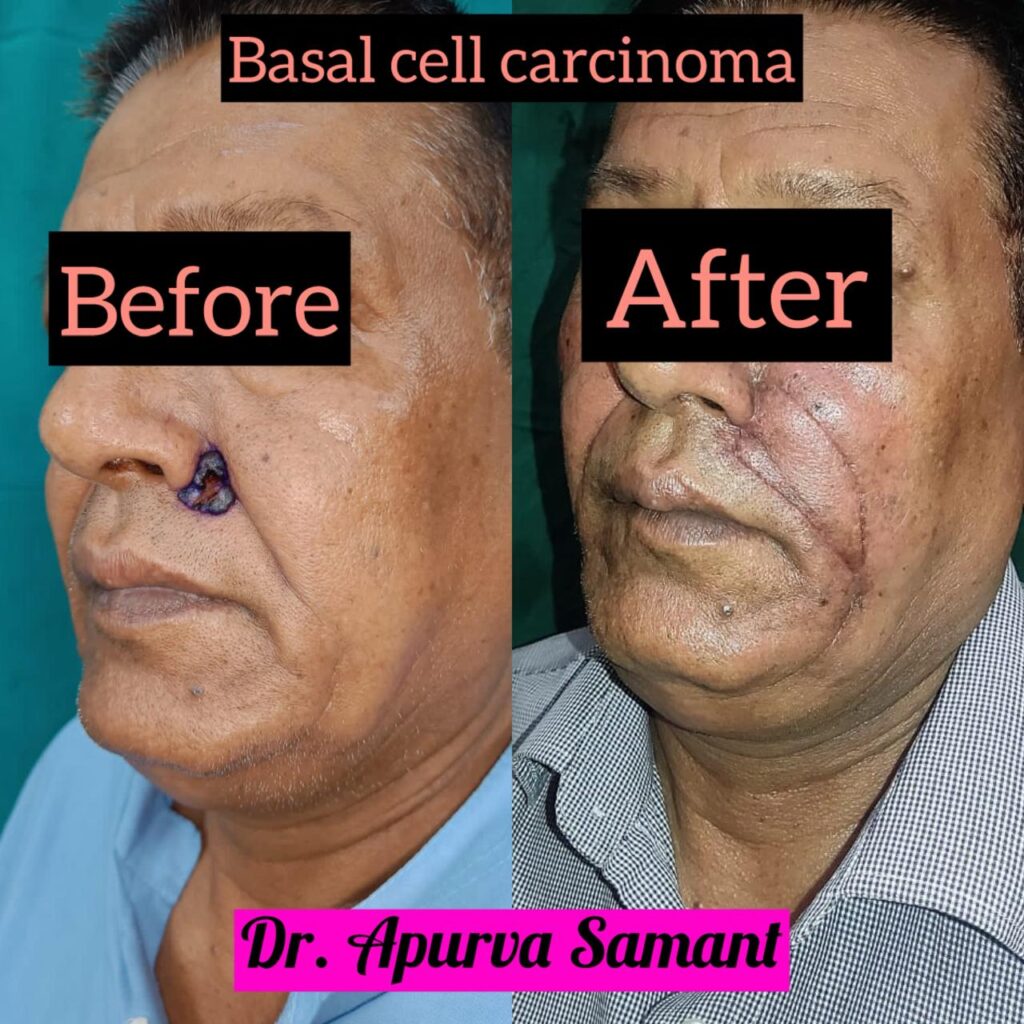
Treatment
Surgery: The most common treatment, involving removal of the cancerous area.
Cryosurgery: Freezing the cancerous tissue to destroy it.
Radiation Therapy: Using radiation to kill cancer cells.
Medications: Topical or systemic medications may be used.
Immunotherapy: Treatments that boost the body’s immune system to fight cancer.
